In the past, Proxmox mainly worked with Virtio disks, which ensured that Windows performed well. Virtio has now been overtaken by virtio-scsi, which provides an even better performance and offers even more functionality, such as TRIM support. Thanks to TRIM, space that is no longer in use in the VM can also be released on the storage cluster.
Unfortunately it is not possible in Windows to just convert a disk from Virtio to SCSI. If you do that, the machine will no longer boot until you restore it to Virtio. This article describes the steps required to ensure that you can safely convert your boot disk. It is important to realize that there are two points where we define how the disk is connected:
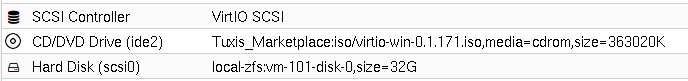
The SCSI Controller and the disk. The SCSI Controller is often set to LSI 53C895A, so we will adjust that!
Roadmap:
- Make a backup
- Make sure your backup is fine
- Delete the snapshots (this is difficult afterwards, because the VM configuration no longer matches)
- Check whether the 'Protection' in the 'Options' tab is disabled
- Configure the Virtio driver CD for the VM. Install the 'vioscsi' drivers
- Switch off the server and change the SCSI Controller to 'VirtIO SCSI' in Proxmox
- Add a new disk (1GB is big enough) of type 'SCSI'.
- Boot the server, go to Computer Management, Disk Management
- Check which disk is the boot disk
- 'Online' the new 1GB disk
- Initialize the 1GB disk
- Create a 'New Simple Volume' on the 1GB disk
- Reboot the server
- Log in and turn off the server
- In Proxmox, Detach the disk(s) and remember which disk is the boot disk
- Double-click on the 'Unused' disks to add them back to the VM and add them as SCSI, check the 'discard' and 'SSD Emulation' checkboxes.
- In Proxmox, click on 'Options' and double-click on 'Boot Order'. Select the correct SCSI disk as the boot disk
- Boot the server
- Check if all desired disks are online
- Shut down the server, remove the temporary disk and boot the server
- If desired, click the 'Protection' checkmark again